Unité de Catalyse et de Chimie du Solide site Artois
Faculté des Sciences de Lens
PUBLICATIONS MARQUANTES 2022 :
- «Morphological, structural, electrical, and piezoelectric analysis of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanowires on various substrates»
A. Hamdi, A. Hamieh, M. Alamri, K. Dogheche, M.M. Saj Mohan, R. Desfeux, D. Rémiens, E. Dogheche
Surfaces and Interfaces 31 (2022) 102103 - doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102103
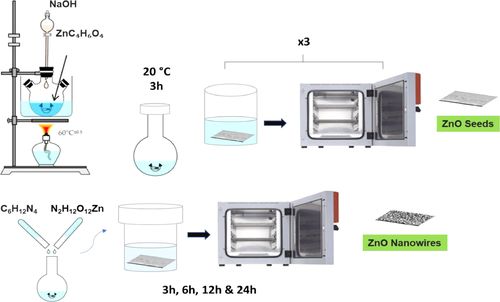 |
| In this present work, we have successfully fabricated a piezoelectric structure based on ZnO nanowires (ZnO NWs) using a simple, low cost and environmentally friendly hydrothermal method. This structure forms the basis to fabricate vertically integrated nanogenerator device. This paper attempts to study the effect of several parameters such as the seed layer morphology, seed layer roughness, seed layer annealing temperature, growth temperature, and growth time on three different substrates, which are silicon substrate with a gold & platinum film as lower metal contact, and stainless steel. The structure and morphology of the seed layer and the as-obtained nanowires were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). SEM analysis shows that the non-aqueous seed solution must be stirred to avoid the formation of the two phases (milky and translucid) and thus the formation of ZnO particles with different sizes and morphologies. In addition, the annealing temperature influences the diameter of the ZnO seed layer and thus ZnO nanowires diameter. This work also shows that the length of the nanowires increases with the growth duration without affecting ZnO diameter (70 ± 30 nm). HR-TEM and XRD studies show the high crystalline quality of the one-dimensional nanomaterials deposited on stainless steel and confirm their high density along the c-axis direction. In this paper, we have also investigated the electrical and piezoelectric performances of the structure obtained. Indeed, the I-V curves exhibit nonlinear and asymmetric electrical characteristics, which confirms the formation of Schottky contacts between the metal and ZnO NWs. According to the piezo-response force microscope, an effective piezoelectric coefficient d33 between 5 and 7 pm/V as a function of the substrate was measured. |
- «Photocatalytic and Photocurrent Responses to Visible Light of the Lone-Pair-Based Oxysulfide Sr6Cd2Sb6S10O7»
S. Al Bacha, S. Saitzek, E. E. McCabe, H. Kabbour
Inorg. Chem., 61, 46 (2022), 18611-18621 - doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03040
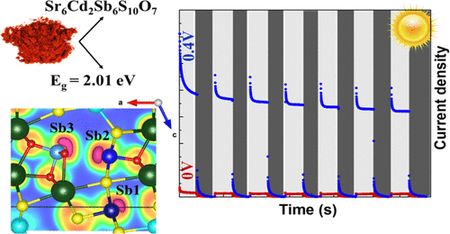 |
| We present a combined experimental and computational study on the recently reported oxysulfide Sr6Cd2Sb6S10O7. Our spectroscopy and photoelectrochemical measurements and tests for photocatalytic activity indicate the potential of Sr6Cd2Sb6S10O7 for photocatalytic applications. In particular, the transient photocurrent response shows a reproducible photogenerated current which depends on light intensity and which indicates an efficient electron–hole separation upon visible light illumination. Density functional theory calculations, combined with crystal orbital Hamiltonian population analysis, give insights into the electronic structure of Sr6Cd2Sb6S10O7 and the origin of its physical properties. Our comprehensive investigation into Sr6Cd2Sb6S10O7 reveals the roles of its polar structure, polar Sb3+ coordination environments, and the 5s2 lone pair in making this compound a potential candidate for solar water splitting photocatalysis. |

- «Catalytic Hydrogenation of Derived Vegetable Oils Using Ion-Exchange Resin-Supported Ruthenium Nanoparticles: Scope and Limitations»
A. Madureira, S. Noël, B. Léger, A. Ponchel, and E. Monflier
ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 50, 16588–16597
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c04178
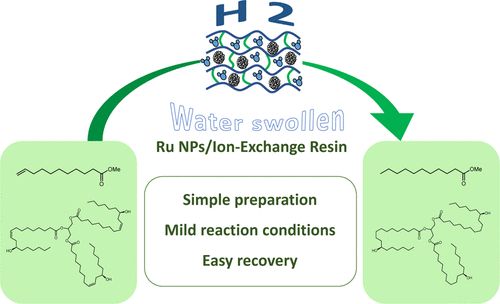 |
| The hydrogenation of vegetable oil-derived compounds using ion-exchange resin-supported ruthenium nanoparticles is reported for the first time. These supported metal catalysts (Ru_DOWEX2-X) were prepared by a simple two-step procedure using commercial and cheap materials, affording high efficiency with a low metal loading. They were characterized by several physicochemical techniques and showed well-dispersed ruthenium nanoparticles into robust beads of the strong cation-exchange resin DOWEX2-X. Their catalytic activity was evaluated for the hydrogenation of methyl undecenoate in heptane under mild experimental conditions (30 °C, 10 bar of H2), and the high activities of the metal solid catalysts deeply depended on the amount of water inside the pores. In terms of recyclability, several physicochemical analyses after successive catalytic runs showed the robustness of the immobilized ruthenium nanoparticles, for which very low metal leaching and no particle aggregation were observed. The decrease in the catalytic activity could be explained by progressive water loss contained in the resin pores, which was illustrated by a decrease in the bead diameter. The immobilized ruthenium nanoparticles were also evaluated in the catalytic hydrogenation of vegetable oils and their corresponding methyl esters and showed a remarkably high activity compared to other catalytic systems tested under similar mild reaction conditions. |

- «Phosphorus-free nitro
gen-containing catalytic systems for hydroformylation and tandem hydroformylation-based reactions»
D.N. Gorbunov, M.V. Nenasheva, M.V. Terenina, Yu. S Kardasheva, E.R. Naranov, A.L. Bugaev, A.V. Soldatov, A.L. Maximov, S. Tilloy, E. Monflier, E.A. Karakhanov
Appl. Catal. A 2022, 647, 118891 - doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118891
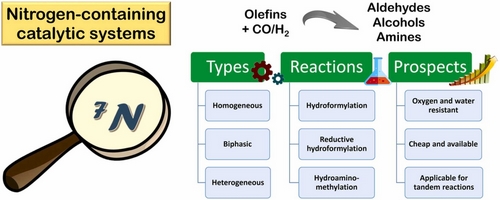 |
| Hydroformylation is an important industrial process applied for the production of many highly-demanded chemicals. For now, only the Co/phosphine, Rh/phosphine, or ligand-free systems are used in industry. Although most of the research dealing with hydroformylation also considers systems with phosphorus-containing ligands or heterogeneous materials, the interest in developing phosphorus-free nitrogen-containing systems tends to grow during the last decade. N-ligands can be easier to synthesize, more stable towards oxidation, and at the same time add some useful features, such as the higher activity in the tandem hydroformylation-based reactions. The review is focused on the progress made in the design of N-ligands for homogeneous and biphasic hydroformylation of unsaturated compounds, as well as N-containing heterogeneous catalysts for the process. In addition, the data on tandem reactions, such as reductive hydroformylation and hydroaminomethylation, are systematized and discussed. |

- «Synthesis of Diols from Jojoba Oil via Rhodium-Catalyzed Reductive Hydroformylation: a Smart Way to Access Biobased Polyurethanes»
C. Becquet, M. Ferreira, H. Bricout, B. Quienne, S. Caillol, E. Monflier and S. Tilloy
Green Chemistry, 2022, 24, 7906–7912 - doi: 10.1039/D2GC02534E
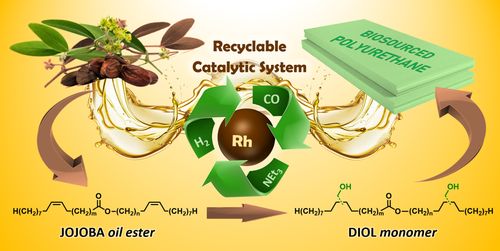 |
| Jojoba oil ester has been functionalized with alcohol groups via hydrohydroxymethylation (HHM) catalyzed by a Rh/amine system. In the optimized conditions, a full conversion together with a 99% yield in alcohol products were obtained. The catalytic system has been recycled via a chromatographic technique at least 10 times without notable loss of activity. The hydrohydroxymethylated products have been succesfully used as monomers for the synthesis of a new biobased polyurethane possessing good thermal and mechanical properties. |

- «Promising Recyclable Ionic Liquid-Soluble Catalytic System for Reductive Hydroformylation»
A. El Mouat, C. Becquet, J. Ternel, M. Ferreira, H. Bricout, E. Monflier, M. Lahcini, and S. Tilloy
ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng 2022, 10, 34, 11310–11319
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c03302
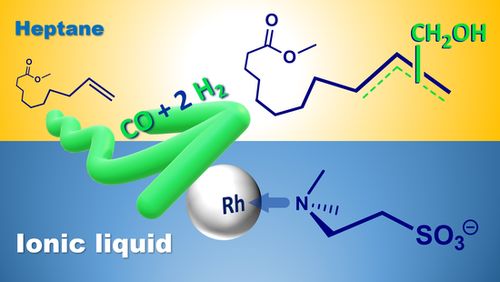 |
| We report here the reductive hydroformylation of methyl 10-undecenoate (issued from castor oil) in a biphasic liquid/liquid system. The rhodium/amine catalytic system is immobilized in an ionic liquid phase, whereas the olefin and the products are in a nonpolar layer. The effects of various reaction parameters (nature and concentration of amines, nature of ionic liquids, temperature and syngas pressure or composition) were studied to increase the production of primary alcohols. Under optimized conditions, potassium N,N-dimethyltaurinate salt associated with rhodium, immobilized in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, allowed us to attain 93% of alcohol yield. With only 2 equiv of amine with respect to rhodium, the catalytic system can be efficiently immobilized in the ionic liquid and recycled due to the ionic nature of the involved catalytic species. |

- «Crystallinity and piezoelectric properties of spray-coated films of P(VDF70-TrFE30): effect of film thickness and spin-crossover nanofillers»
J-E. Angulo Cervera, M. Piedrahita-Bello, B. Martin, E. Dantras, L. Nicu, T. Leichlé, K. Dalla Francesca, A. Da Costa, A. Ferri, R. Desfeux, L. Salmon, G. Molnar and A. Bousseksou
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 8466-8473 - doi: 10.1039/D2TC01162J
 |
| Spray coating the ferroelectric polymer P(VDF-TrFE) appears as an attractive approach for the fabrication of electromechanical transducers. However, it is important to elucidate how the crystallinity and associated piezoelectric properties depend on the coating thickness and additives. To this aim, we have spray-coated various substrates both with pure and nanocomposite films of the 70-30 % copolymer in a broad thickness range (200 nm – 30 µm). Using X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy, we show that the obtained films are dense and homogeneous with ca. 50-60 % crystallinity, which consists of a majority polar β-phase, with slight alterations in the sub-micrometer thickness regime. Robust piezoelectricity and ferroelectricity are revealed at room temperature through both local hysteresis loops and lithography experiments using the piezoresponse force microscopy technique. After poling, the piezoelectric d33 coefficient displays values up to -19 and -11 pC/N for the pure copolymer and the composite, respectively. For a 33 vol% load of inorganic spin-crossover nanofiller, the switching properties are substantially improved and a coercive voltage <10 V is demonstrated for micrometric films. Overall, this approach appears as a promising way for the in-situ integration of high quality piezopolymer films into complex transducer geometries for sensing, actuating and energy harvesting purposes. |

- «Interesterification of triglycerides with methyl acetate for biodiesel production using a cyclodextrin-derived SnO@γ-Al2O3 composite as heterogeneous catalyst»
C. Prestigiacomo, M. Biondo, A. Galia, E. Monflier, A. Ponchel, D. Prevost, O. Scialdone, S. Tilloy, R. Bleta
Fuel 321 (2022) 124026 - doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124026
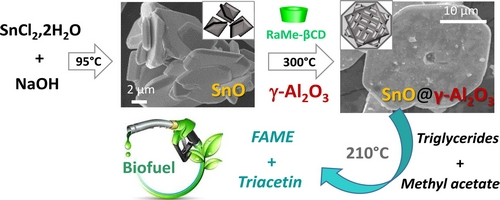 |
| Particle morphology and surface properties of metal oxides are topics of great importance in the field of heterogeneous catalysis. Herein, we have developed a molecular-colloidal coassembly approach combined with an ultrasonic-assisted precipitation method to fabricate SnO@γ-Al2O3 composites with tuneable pore size and well-defined octahedral-shape crystal structure. The supramolecular assemblies formed between the randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin (RaMeβCD) and Pluronic F127 were employed as template to tailor the size and shape of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles and direct their assembly almost exclusively on the surface of micrometer-sized SnO single crystals. Results revealed that the cooperative action of the supramolecular template and γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles may have a critical effect on the growth and orientation of SnO microcrystals and ultimately determine their catalytic performance in the interesterification of rapeseed oil with methyl acetate. The compartmentalized SnO@γ-Al2O3 structures could achieve fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) and triacetin (TA) yields of 33.5% and 1.5% respectively after 30 min at 210 °C, exceeding by 38% the FAME yield of the commercial catalyst. |

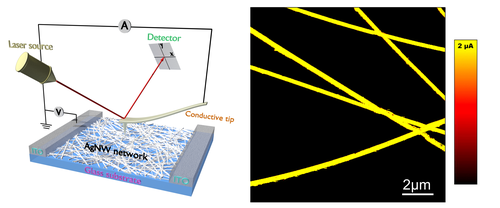
- «Nanoscale electrical investigation of transparent conductive electrodes Based on silver nanowire network»
S. H. Pham, A. Ferri, A. Da Costa, M. M. Saj Mohan, V. D. Tran, D. C. Nguyen, P. Viville, R. Lazzaroni, R. Desfeux, P. Leclère
Adv Mater Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200019 - doi: 10.1002/admi.202200019 Article in cover
 |
 |
|
|
Presently, metallic nanowires (NWs) are the most promising materials to fabricate flexible transparent electrodes as an alternative to indium tin oxide. Here, the high performance of transparent conductive electrodes (TCEs) based on silver nanowires (AgNWs) percolation networks is reported. With optimized experimental conditions for the deposition, the AgNWs result in low sheet resistance of 10 Ω sq−1 combined with a high optical transmittance of 92.6% at λ = 550 nm. This leads to a valuable figure of merit as compared to other TCEs. In this study, the nanoscale electrical properties of the AgNWs are measured via conductive atomic force microscopy to characterize the percolation network. The electrical resistivity value calculated for a single AgNW is found to be about 12.35 µΩ cm, while a nanoscale conductivity map over an AgNW network bridging two electrodes has revealed high levels of current within the network over a distance of more than 1000 µm. The favorable determined conductivity results along with the high optical properties of the AgNWs network strongly suggest that thin-film electrodes based on AgNWs will be a potential approach for future flexible electronic devices. |

- « Unnatural cyclodextrins can be accessed from enzyme-mediated dynamic combinatorial libraries»
D. Larsen, M. Ferreira, S. Tilloy, E. Monflier, S.R. Beeren
Chem. Comm. 2022, 58, 2287-2290 - doi: 10.1039/D1CC06452E
This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Communications HOT Articles 2022
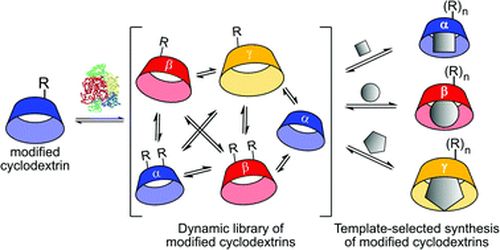 |
| Dynamic systems of cyclodextrins (CDs) enabled by a native cyclodextrin glucanotransferase (CGTase) can incorporate unnatural glucopyranose-derived building blocks, expanding the applicability of enzyme-mediated dynamic combinatorial chemistry by using synthetically modified substrates. Starting dynamic combinatorial libraries from CDs with a single 6-modified glucopyranose results in a dynamic mixture of CDs containing several modified glucopyranoses. The relative concentrations of modified α, β or γ-CDs can be controlled by the addition of templates, providing a novel way to access modified CDs. |

- « An unusual O2-/F- distribution in the new pyrochlore oxyfluorides: Na2B2O5F2 (B= Nb, Ta)»
E. Boivin, F. Pourpoint, S. Saitzek, P. Simon, P. Roussel, H. Kabbour
Chem. Comm., 2022, 58, 2391-2394 - doi: 10.1039/D1CC06760E
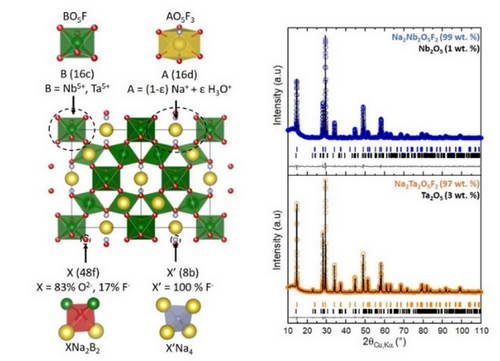 |
| Two new oxyfluorides with a pyrochlore-type structure, Na2Nb2O5F2 and Na2Ta2O5F2, have been obtained and for which the XRD crystallographic study coupled with 19F solid state NMR reveals an unusual O/F distribution. Both materials are n-type semiconductors exhibiting photoconductive properties. |

Faculté Jean Perrin - rue Jean Souvraz - SP 18 - 62307 Lens Cedex
tel : 03 21 79 17 05
fax : 03 21 79 17 55 |